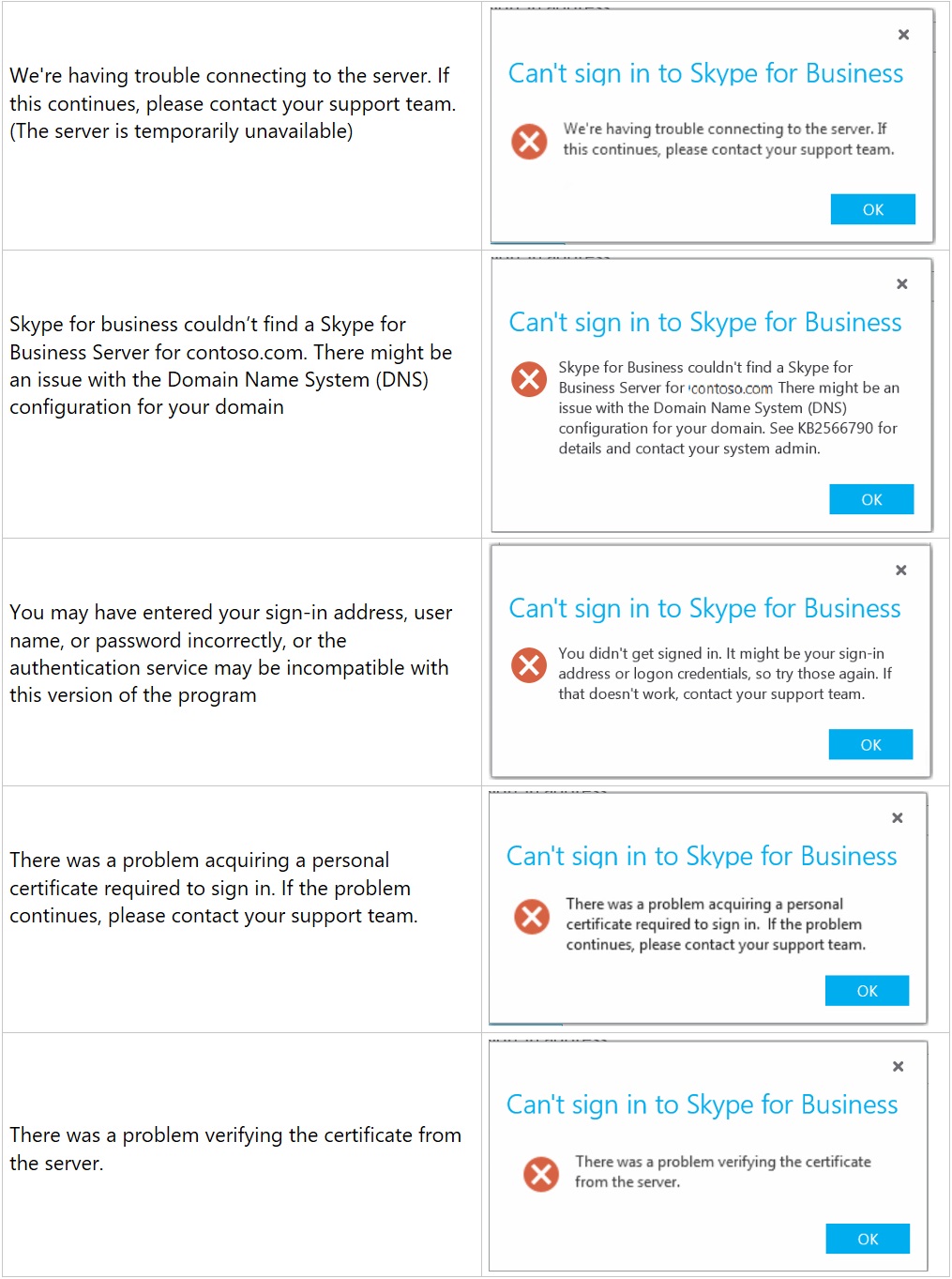
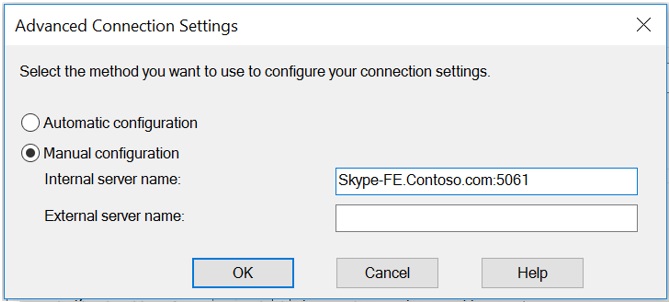
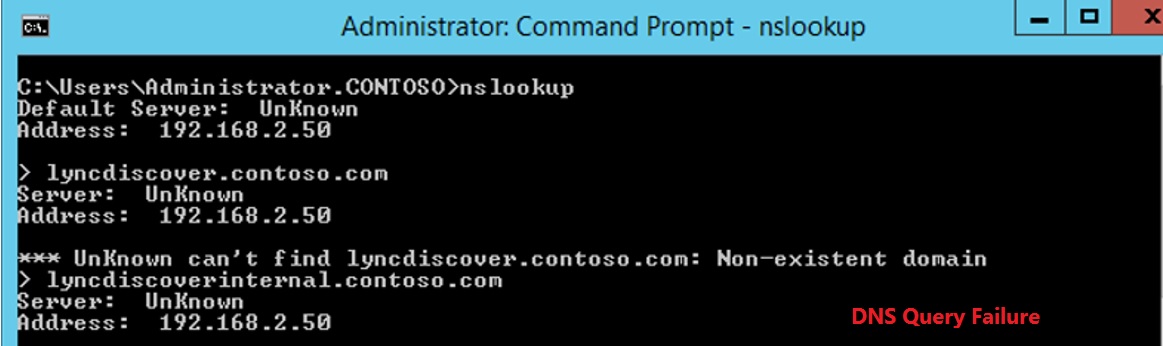
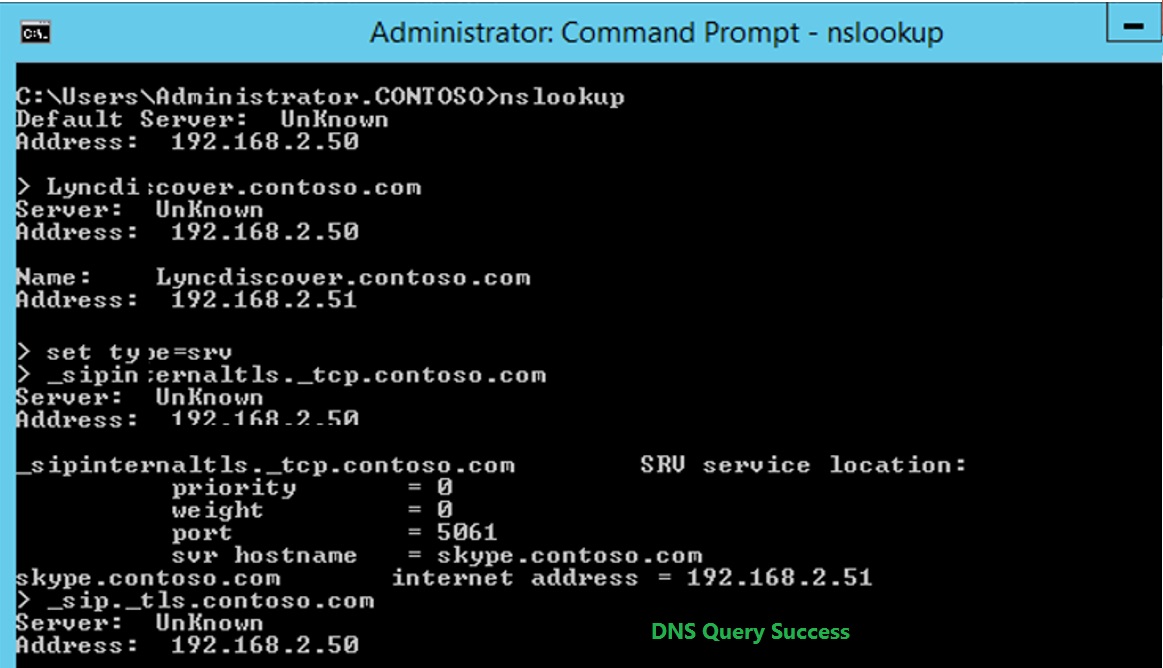
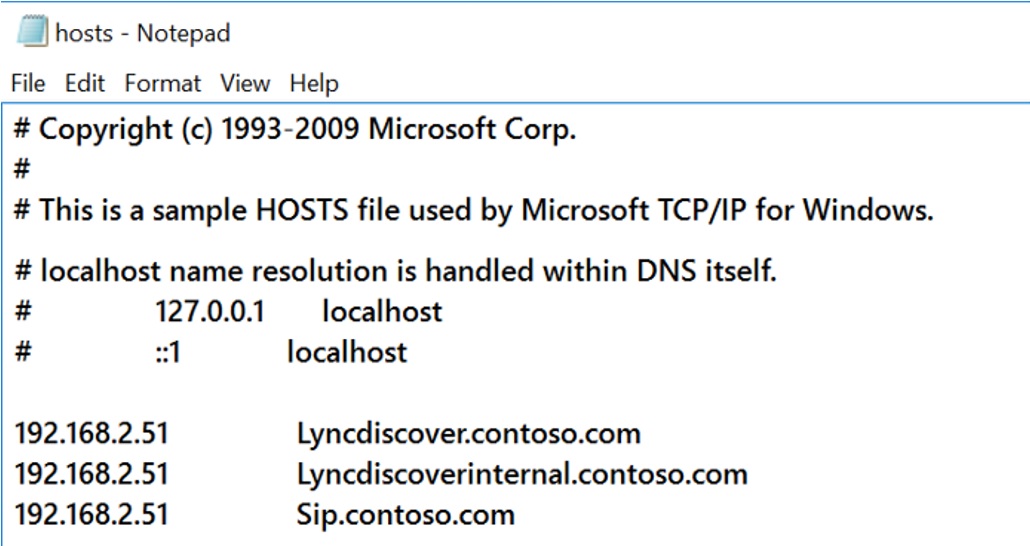
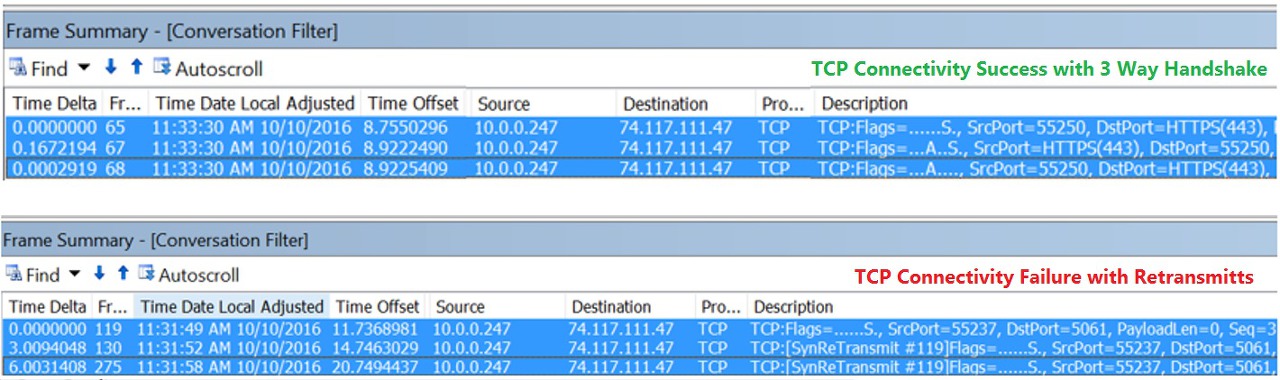
Now that I have outlined the building blocks of a Lync infrastructure, there are three more topics to understand if we want to have a working infrastructure:
- Firewall rules required to allow communications for Lync clients, Lync servers and for the aforementioned non-Lync servers with additional services we need
- DNS settings to make Lync services available both on the internal network and from the Internet
- Structure of the certificates. Lync is secure by design and digital certificates are mandatory for every Lync 2013 infrastructure
Firewall Rules Required for Lync Server 2013
A deep dive about firewall rules for Lync Server 2013 should include TechNet article Port Requirements http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg398798.aspx and the Lync 2013 Protocol Workloads poster http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=39968 (i.e. to check the requirements for the different scenarios). However to make the topic easier to understand, I have tried to create an explanation based on some assumption.
- The first assumption I will make here is that your network has a segregated DMZ to make services available to the Internet in a secure manner. A couple of the possible solutions for such a deployment are
- Using two firewalls. Note: usually the technology used for the firewalls is not important. However if a SIP trunk is required in our scenario, it is important to have a SIP Application-level gateway (ALG).
- A three-legged firewall that will create a logical demilitarized zone
There is no difference in the result, from the functionality point of view, going for the first option or the second one. A single firewall would imply a single point of failure and higher security risk, because a single Internet-connected device will be exposed both on the DMZ and on the internal network. Having two different firewalls, a front (FW2) and a back firewall (FW1), as shown in figure 6.7, is more secure, especially if we are going to use two different platforms or solutions for security. In the aforementioned scenario, an exploitable security vulnerability on a single technology will not affect the second firewall
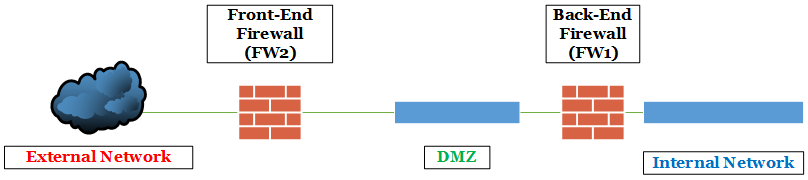
A layout including only firewalls and networks that will have an impact on our Lync deployment
Figure 6.7 layout including only firewalls and networks that will have an impact on our Lync deployment
- The second assumption will be that we will not deploy High Availability or load balancing systems (including Enterprise Edition pools of Lync Front Ends). Although you may require them in a real-world design, they add a configuration overhead that will not help understanding the fundamentals of Lync Server 2013 network traffic requirements
- The third assumption is that we will use NAT every time that a public IP is required. Exposing directly a server to the Internet usually is not the best security solution available
- Fourth assumption is that the Edge Server will use three addresses on the “external” network interface card to expose services to the Internet. The addresses are the ones we have already seen:

Edge_IPs
- Last assumption: no integration or connection with Office Communications Server 2007 deployments or clients is required
We will have to grant the following types of network traffic:
6.1 From servers in the DMZ to servers in the internal network
6.2 From servers in the DMZ to the external network
6.3 From the external network to servers in the DMZ
6.4 From servers in internal network to servers in DMZ
6.5 Network traffic related to Lync clients in the internal network
Note: the point 6.5 of the list is interesting only if you have firewalls (or end-point firewalls) separating the networks containing the Lync clients and the Lync servers.
6.1 Network Traffic from servers in The DMZ to Servers in the Internal Network
On the Back-End firewall, FW1,for traffic starting from the reverse proxy, the following ports will be required
|
Reverse proxy Rules on Back-End firewall (FW1) |
|||||
| Source Interface | Protocol | Source Port | Destination Port | Destination | Service |
| Internal NIC of the reverse proxy | TCP (HTTPS) | Any | 4443 | Lync Front End | Web Services on the Lync Front End |
| Internal NIC of the reverse proxy | TCP(HTTPS) | Any | 443 | Office Web Apps Server | PowerPoint presentation sharing |
On the Back-End firewall, FW1, for traffic starting from the Edge Server, the following ports will be required
|
Lync Edge Server Rules on Back-End firewall (FW1) |
|||||
|
Source Interface |
Protocol |
Source Port |
Destination Port |
Destination |
Service |
| Internal NIC of the Edge | TCP (SIP/MTLS) | Any | 5061 | Lync Front End | Inbound SIP traffic |
6.2 Network Traffic from Servers in the DMZ to the External Network
On the Front firewall, FW2, from the Edge Server, the following ports will be required. It is helpful to remind you the fourth assumption: we have three different IPs on the external network interface of the Lync Edge Server: Access, Webconf and AV. The firewall rules for network traffic from the external network to the Edge will have to point to one of the three IPs, as explained in the following table.
|
Lync Edge Server Rules on Front-End firewall (FW2) |
|||||
| Source Interface | Protocol | Source Port | Destination Port | Destination | Service |
| External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | TCP (XMPP) | Any | 5269 | To federated XMPP partners | Standard server-to-server communication port for XMPP |
| External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | TCP (SIP/MTLS) | Any | 5061 | Federation Services and Partners | Lync and Skype Federation using SIP |
| External NIC of the Edge (AV IP) | UDP (Stun/Turn) | Any | 3478 | Any | Stun/Turn negotiation for candidates |
| External NIC of the Edge (AV IP) | TCP (Stun/Turn) | Any | 443 | Any | Stun/Turn negotiation for candidates |
6.3 Network Traffic from the External Network to Servers in the DMZ
On the Front firewall, FW2, traffic from the external network to the reverse proxy, the following ports will be required
|
To the reverse proxy from the external network on Front-End firewall (FW2) |
|||||
| Source Interface | Protocol | Source Port | Destination Port | Destination | Service |
| Any | TCP (HTTPS) | Any | 443 | Reverse proxy external network interface | Access to the web services on the Lync Front End |
On the Front-End firewall, FW2, traffic from the external network to the Edge Server, the following ports will be required
|
To the Lync Edge from the external network on Front-End firewall (FW2) |
|||||
| Source Interface | Protocol | Source Port | Destination Port | Destination | Service |
| Any | TCP (SIP/TLS) | Any | 443 | External NIC of the Edge (Webconf IP) | Web Conferencing Media |
| Any | TCP (SIP/TLS) | Any | 443 | External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | Client-to-server SIP traffic for external user access |
| Federated XMPP partners | TCP (XMPP) | Any | 5269 | External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | Standard server-to-server communication port for XMPP |
| Federation Services and Partners | TCP (SIP/MTLS) | Any | 5061 | External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | Lync and Skype Federation using SIP |
| Any | UDP (Stun/Turn) | Any | 3478 | External NIC of the Edge (AV IP) | Stun/Turn negotiation for candidates |
| Any | TCP (Stun/Turn) | Any | 443 | External NIC of the Edge (AV IP) | Stun/Turn negotiation for candidates |
6.4 Network Traffic from Servers in the Internal Network to Servers in the DMZ
On the Back-End firewall, FW1, for traffic starting from the internal network, the following ports will be required
|
To the Lync Edge from the internal network on Back-End firewall (FW1) |
|||||
| Source Interface | Protocol | Source Port | Destination Port | Destination | Service |
| Lync Front End | TCP (XMPP/MTLS) | Any | 23456 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Outbound XMPP traffic |
| Lync Front End | TCP (SIP/MTLS) | Any | 5061 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Outbound SIP traffic |
| Lync Front End | TCP (PSOM/MTLS) | Any | 8057 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Web conferencing traffic |
| Lync Front End | TCP (SIP/MTLS) | Any | 5062 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Authentication of A/V users |
| Lync Front End | TCP (HTTPS) | Any | 4443 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Replication of CMS on the Lync Edge |
| Lync Front End | TCP (Stun/Turn) | Any | 443 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Stun/Turn negotiation for candidates |
6.5 Network Traffic Related to Lync Clients in the Internal Network
The following rules are required on any end-point firewall and on any internal firewall that controls traffic coming from the Lync clients on the internal network.
| From | To | Feature |
Protocol |
Port | Bidirectional | Note |
| Internal Client | Lync Front End | Presence and IMAV and Web ConferencingApplication SharingEnterprise Voice |
SIP/TLS |
5061 |
||
| Presence and IMAV and Web Conferencing |
HTTPS |
443 |
||||
| Enterprise Voice |
STUN/TCP |
|||||
| AV and Web ConferencingApplication Sharing |
SRTP/UDP |
49152-65535 |
||||
| AV and Web Conferencing |
PSOM/TLS |
8057 |
||||
| Enterprise Voice |
TURN/TCP |
448 |
||||
| Enterprise Voice |
UDP |
3478 |
||||
| Internal Client A | Internal Client B | AV and Web ConferencingApplication Sharing |
SRTP/UDP |
1024-65535 |
Yes |
Peer to Peer Sessions |
| Internal Client | Lync Edge | AV and Web ConferencingApplication Sharing |
STUN/TCP |
443 |
||
| Enterprise Voice |
TURN/TCP |
|||||
| AV and Web Conferencing |
UDP |
3478 |
||||
| Internal Client | Exchange UM | Enterprise Voice |
SRTP/RTCP |
60000-64000 |
Yes |
|
| Internal Client | Voice Gateway | Enterprise Voice |
SRTP/RTCP |
30000-39999 |
With Media Bypass | |
| Internal Client | Director | Presence and IM |
SIP/TLS |
5061 |
||
Notes Related to the Firewall Rules Required for Lync Server 2013
Lync Server 2013 Edge Server requires DNS resolution and http access to revocation lists of certificates. Depending from your network design, the aforementioned services could be on the Internet or could be available using services on the internal network (like a proxy). The following rule is to be adapted to your network layout
|
Additional Lync Edge Server Rules on Front-End firewall (FW2) or on Back-End firewall (FW1) |
|||||
| Source Interface | Protocol | Source Port | Destination Port | Destination | Service |
| External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | TCP | Any | 53 | DNS servers for DMZ | DNS resolution |
| External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | UDP | Any | 53 | DNS servers for DMZ | DNS resolution |
| External NIC of the Edge (Access IP) | TCP (HTTP) | Any | 80 | Depends on the HTTP navigation service available | CRL verifications |
Centralized Logging Service (a new feature in Lync Server 2013) requires additional ports on the back-end firewall (for more details see the TechNet article Using the Centralized Logging Service http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj688101.aspx
|
Lync Edge Server Rules on Back-End firewall (FW1) for centralized logging |
|||||
| Source Interface | Protocol | Source Port | Destination Port | Destination | Service |
| Centralized Logging Service | TCP (MTLS) | Any | 50001 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Centralized Logging Service |
| Centralized Logging Service | TCP (MTLS) | Any | 50002 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Centralized Logging Service |
| Centralized Logging Service | TCP (MTLS) | Any | 50003 | Internal NIC of the Edge | Centralized Logging Service |
Disclaimer: please consider the answer as an approximation that could miss some detail. I will try to make a more complete answer in a future post.
Ports required in Lync 2013 (must be reachable from your administrative workstation):
— Ports LDAP (TCP 389) and msft-gc (TCP 3268) on a global catalog/domain controller are always required
-For the Lync Server Control Panel (process is AdminUIHost.exe): HTTPS and TCP 49336 on the Lync server you are going to manage
-For the Lync Server Management Shell (process is powershell.exe): TCP 49336 on the Lync server you are going to manage
-For the Topology Builder to download Lync topology (process is Microsoft.Rtc.Management.TopologyBuilder.exe): TCP 49336 on the Lync server hosting the CMS database
-For the Topology Builder to publish Lync topology (process is Microsoft.Rtc.Management.TopologyBuilder.exe): in addition to the aforementioned ports, Microsoft Directory Services TCP/UDP 445 to a Domain Controller and to the Lync server hosting the CMS database
Part 2 of the draft: Chapter 6 DNS, Certificate and Firewall Requirements for Lync Server 2013 – Absolute U.C.
Infrastructure requirements Now that I have outlined the building blocks of a Lync infrastructure, there are three more topics to understand if we want to have a working infrastructure: Firewall rules required to allow communications for Lync clients, Lync
www.absoluteuc.org
'IT이야기 > S4B&Lync' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 1 부 : Skype® for Business 2015 - SfB - (Lync® 2013) 배포 방법 (0) | 2019.08.02 |
|---|---|
| Lync Server 2013 Cumulative Update List: June 2019 (1) | 2019.07.24 |
| LyncServer2013및 SkypeforBusinessServer2015의 사용자 복제자 이해 (0) | 2019.07.23 |
| LyncServer2010의 SecurityGroup (0) | 2019.07.17 |
| Troubleshooting Skype for Business Client sign in issues (0) | 2019.07.09 |