This article describes minimum hardware requirements for Storage Spaces Direct. For hardware requirements on Azure Stack HCI, our operating system designed for hyperconverged deployments with a connection to the cloud, see Before you deploy Azure Stack HCI: Determine hardware requirements.
For production, Microsoft recommends purchasing a validated hardware/software solution from our partners, which include deployment tools and procedures. These solutions are designed, assembled, and validated against our reference architecture to ensure compatibility and reliability, so you get up and running quickly. For hardware solutions, visit the Azure Stack HCI solutions website.
Tip
Want to evaluate Storage Spaces Direct but don't have hardware? Use Hyper-V or Azure virtual machines as described in Using Storage Spaces Direct in guest virtual machine clusters.
Base requirements
Systems, components, devices, and drivers must be certified for the operating system you’re using in the Windows Server Catalog. In addition, we recommend that servers and network adapters have the Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) Standard and/or Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) Premium additional qualifications (AQs), as pictured below. There are over 1,000 components with the SDDC AQs.
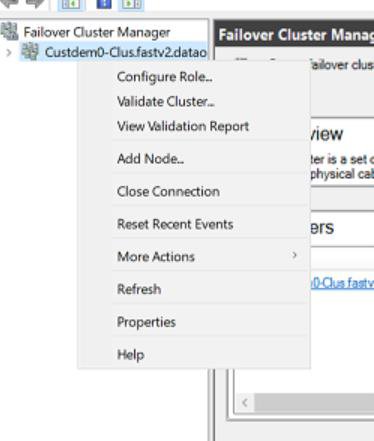
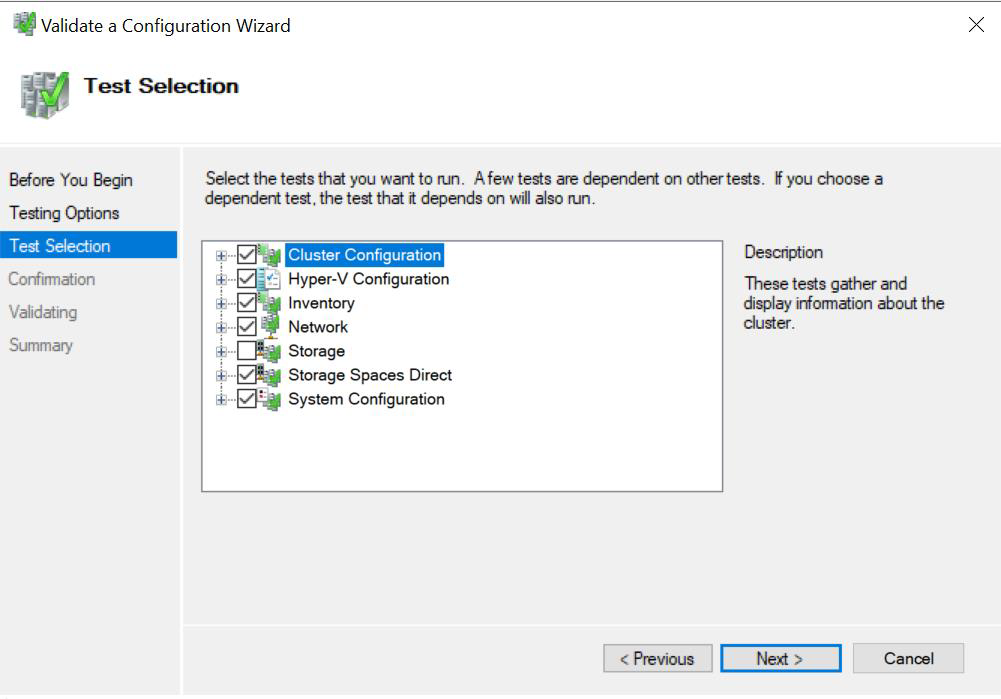
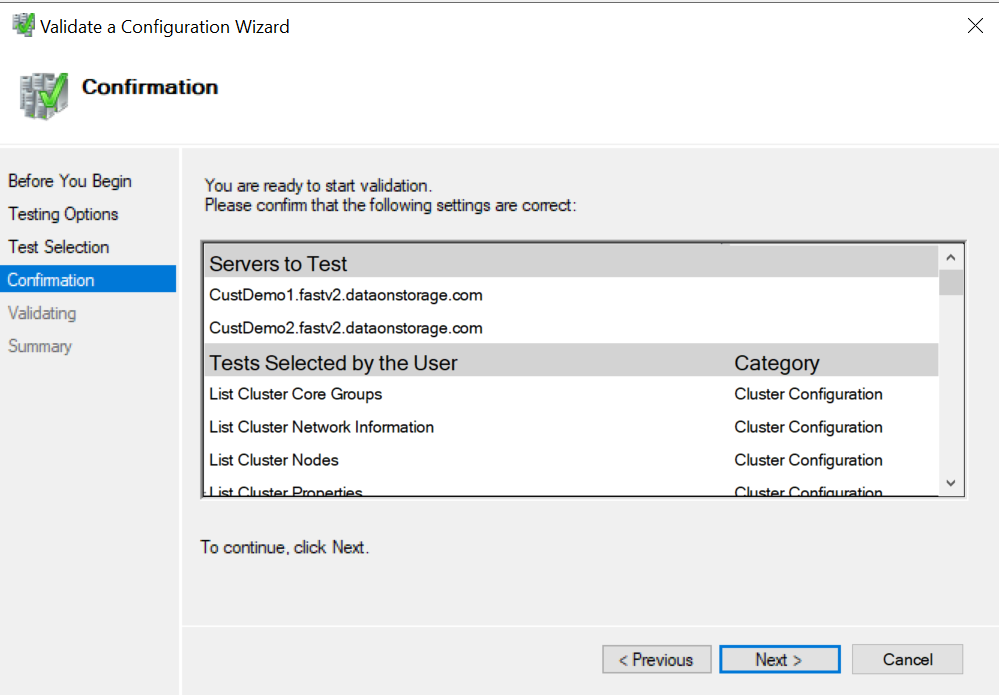
The fully configured cluster (servers, networking, and storage) must pass all cluster validation tests per the wizard in Failover Cluster Manager or with the Test-Cluster cmdlet in PowerShell.
In addition, the following requirements apply:
Servers
- Minimum of 2 servers, maximum of 16 servers
- Recommended that all servers be the same manufacturer and model
CPU
- Intel Nehalem or later compatible processor; or
- AMD EPYC or later compatible processor
Memory
- Memory for Windows Server, VMs, and other apps or workloads; plus
- 4 GB of RAM per terabyte (TB) of cache drive capacity on each server, for Storage Spaces Direct metadata
Boot
- Any boot device supported by Windows Server, which now includes SATADOM
- RAID 1 mirror is not required, but is supported for boot
- Recommended: 200 GB minimum size
Networking
Storage Spaces Direct requires a reliable high bandwidth, low latency network connection between each node.
Minimum interconnect for small scale 2-3 node
- 10 Gbps network interface card (NIC), or faster
- Two or more network connections from each node recommended for redundancy and performance
Recommended interconnect for high performance, at scale, or deployments of 4+
- NICs that are remote-direct memory access (RDMA) capable, iWARP (recommended) or RoCE
- Two or more network connections from each node recommended for redundancy and performance
- 25 Gbps NIC or faster
Switched or switchless node interconnects
- Switched: Network switches must be properly configured to handle the bandwidth and networking type. If using RDMA that implements the RoCE protocol, network device and switch configuration is even more important.
- Switchless: Nodes can be interconnected using direct connections, avoiding using a switch. It's required that every node has a direct connection with every other node of the cluster.
Drives
Storage Spaces Direct works with direct-attached SATA, SAS, NVMe, or persistent memory (PMem) drives that are physically attached to just one server each. For more help choosing drives, see the Choosing drives and Understand and deploy persistent memory articles.
- SATA, SAS, persistent memory, and NVMe (M.2, U.2, and Add-In-Card) drives are all supported
- 512n, 512e, and 4K native drives are all supported
- Solid-state drives must provide power-loss protection
- Same number and types of drives in every server – see Drive symmetry considerations
- Cache devices must be 32 GB or larger
- Persistent memory devices are used in block storage mode
- When using persistent memory devices as cache devices, you must use NVMe or SSD capacity devices (you can't use HDDs)
- If you're using HDDs to provide storage capacity, you must use storage bus caching. Storage bus caching isn't required when using all-flash deployments
- NVMe driver is the Microsoft-provided one included in Windows (stornvme.sys)
- Recommended: Number of capacity drives is a whole multiple of the number of cache drives
- Recommended: Cache drives should have high write endurance: at least 3 drive-writes-per-day (DWPD) or at least 4 terabytes written (TBW) per day – see Understanding drive writes per day (DWPD), terabytes written (TBW), and the minimum recommended for Storage Spaces Direct
Note
When using all flash drives for storage capacity, the benefits of storage pool caching will be limited. Learn more about the storage pool cache.
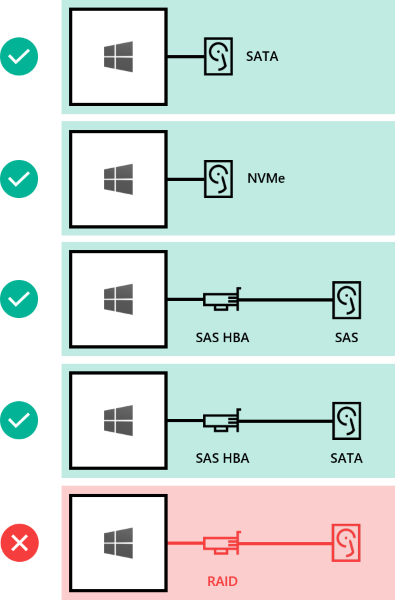
Here's how drives can be connected for Storage Spaces Direct:
- Direct-attached SATA drives
- Direct-attached NVMe drives
- SAS host-bus adapter (HBA) with SAS drives
- SAS host-bus adapter (HBA) with SATA drives
- NOT SUPPORTED: RAID controller cards or SAN (Fibre Channel, iSCSI, FCoE) storage. Host-bus adapter (HBA) cards must implement simple pass-through mode for any storage devices used for Storage Spaces Direct.
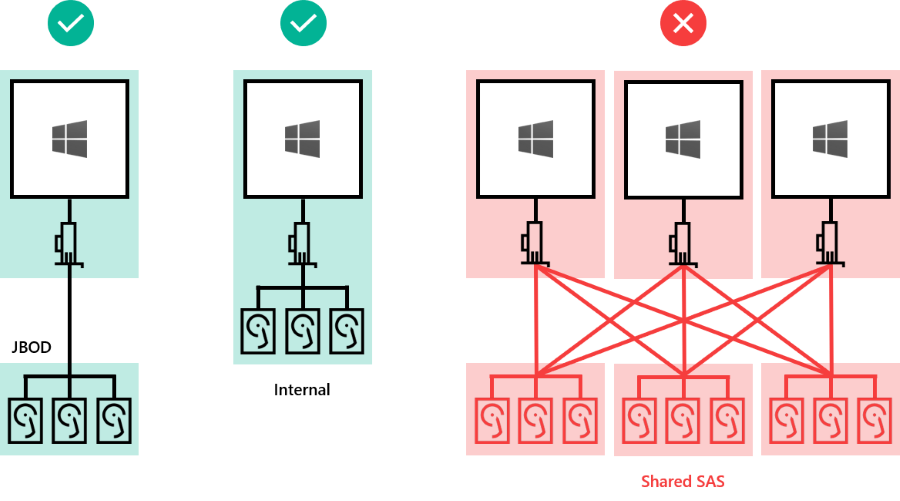
Drives can be internal to the server, or in an external enclosure that is connected to just one server. SCSI Enclosure Services (SES) is required for slot mapping and identification. Each external enclosure must present a unique identifier (Unique ID).
- Drives internal to the server
- Drives in an external enclosure ("JBOD") connected to one server
- NOT SUPPORTED: Shared SAS enclosures connected to multiple servers or any form of multi-path IO (MPIO) where drives are accessible by multiple paths.
Minimum number of drives (excludes boot drive)
The minimum number of capacity drives you require varies with your deployment scenario. If you're planning to use the storage pool cache, there must be at least 2 cache devices per server.
You can deploy Storage Spaces Direct on a cluster of physical servers or on virtual machine (VM) guest clusters. You can configure your Storage Spaces Direct design for performance, capacity, or balanced scenarios based on the selection of physical or virtual storage devices. Virtualized deployments take advantage of the private or public cloud's underlying storage performance and resilience. Storage Spaces Direct deployed on VM guest clusters allows you to use high availability solutions within virtual environment.
The following sections describe the minimum drive requirements for physical and virtual deployments.
Physical deployments
This table shows the minimum number of capacity drives by type for hardware deployments such as Azure Stack HCI version 21H2 or later, and Windows Server.
| All persistent memory (same model) | 4 persistent memory | 2 persistent memory |
| All NVMe (same model) | 4 NVMe | 2 NVMe |
| All SSD (same model) | 4 SSD | 2 SSD |
If you're using the storage pool cache, there must be at least 2 more drives configured for the cache. The table shows the minimum numbers of drives required for both Windows Server and Azure Stack HCI deployments using 2 or more nodes.
| Persistent memory + NVMe or SSD | 2 persistent memory + 4 NVMe or SSD |
| NVMe + SSD | 2 NVMe + 4 SSD |
| NVMe + HDD | 2 NVMe + 4 HDD |
| SSD + HDD | 2 SSD + 4 HDD |
Important
The storage pool cache cannot be used with Azure Stack HCI in a single node deployment.
Virtual deployment
This table shows the minimum number of drives by type for virtual deployments such as Windows Server guest VMs or Windows Server Azure Edition.
| Virtual Hard Disk | 2 |
Tip
To boost the performance for guest VMs when running on Azure Stack HCI or Windows Server, consider using the CSV in-memory read cache to cache unbuffered read operations.
If you're using Storage Spaces Direct in a virtual environment, you must consider:
- Virtual disks aren't susceptible to failures like physical drives are, however you're dependent on the performance and reliability of the public or private cloud
- It's recommended to use a single tier of low latency / high performance storage
- Virtual disks must be used for capacity only
Learn more about deploying Storage Spaces Direct using virtual machines and virtualized storage.
Maximum capacity
| Raw capacity per server | 400 TB | 100 TB |
| Pool capacity | 4 PB (4,000 TB) | 1 PB |
'IT이야기 > Hyper-V' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Adding servers or drives to Storage Spaces Direct (0) | 2022.11.29 |
|---|---|
| Adding servers or drives to Storage Spaces Direct (0) | 2022.11.29 |
| Adding servers or drives to Storage Spaces Direct (0) | 2022.11.29 |
| Best Practice in Taking an S2D Server Offline for Maintenance (0) | 2022.11.29 |
| How to Run Cluster Validation in Failover Cluster Manager Prin (0) | 2022.11.29 |