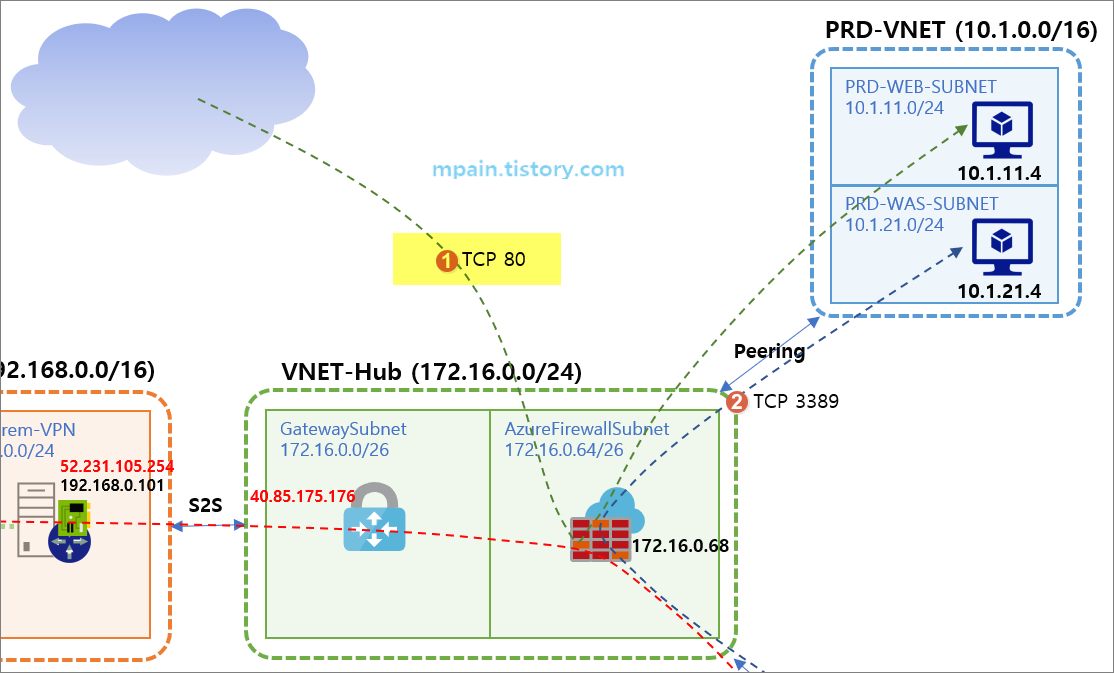
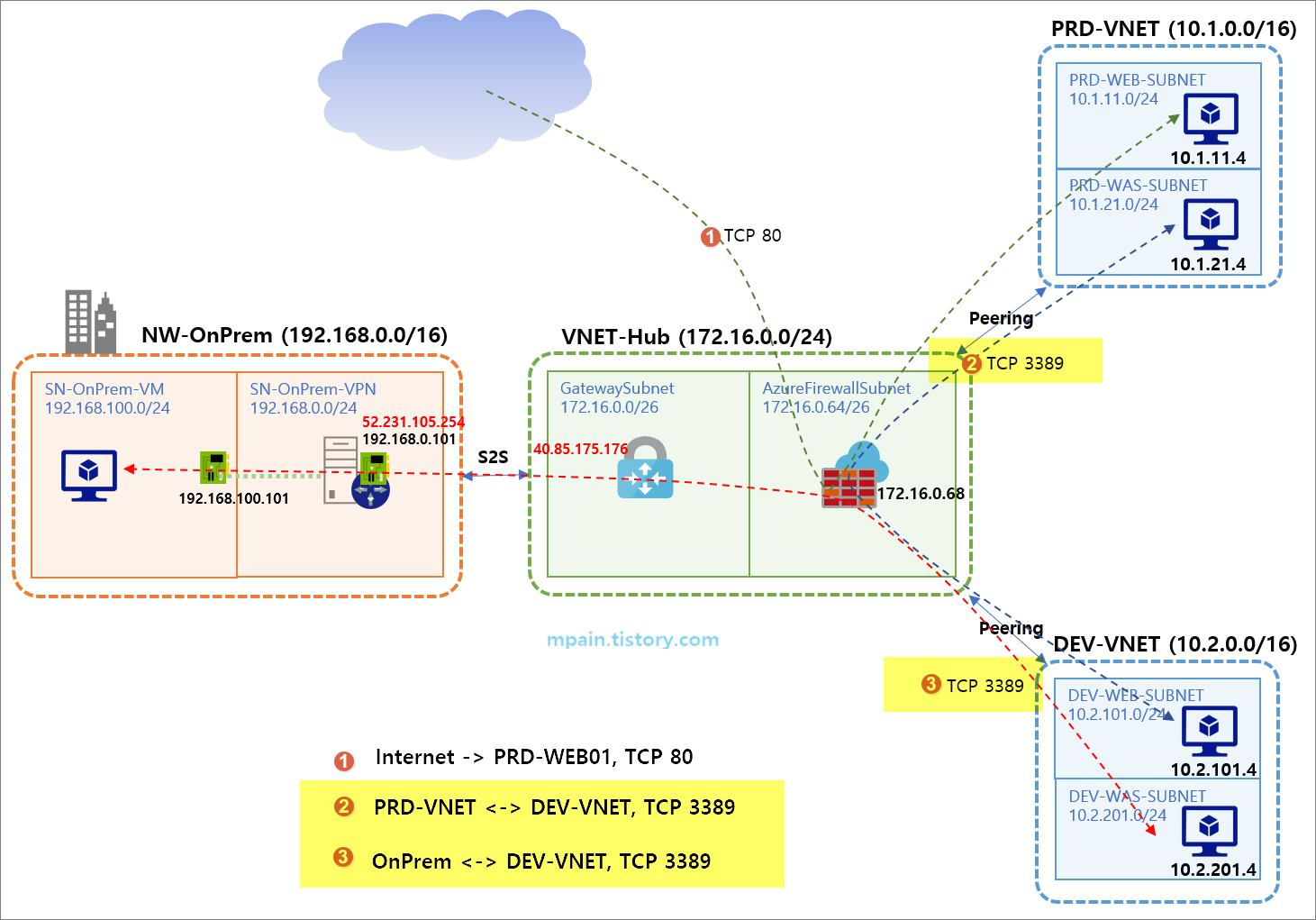
Azure 가상 네트워크에 Azure Firewall을 배포하고, 가상 네트워크 간 라우팅, DNAT, 네트워크 필터링 규칙을 구성하는 방법을 설명합니다.
아래와 같은 테스트 환경을 구성하고 Azure Firewall을 테스트하였습니다.
- 허브(Hub) 네트워크에 Azure Firewall을 배치하여 스포크(Spoke) 네트워크 간 라우팅 처리
- Azure Firewall의 DNAT 규칙으로 인터넷 인바운드 처리
- Azure Firewall의 네트워크 규칙(Network rule)으로 스포크 네트워크 간 RDP 연결 처리
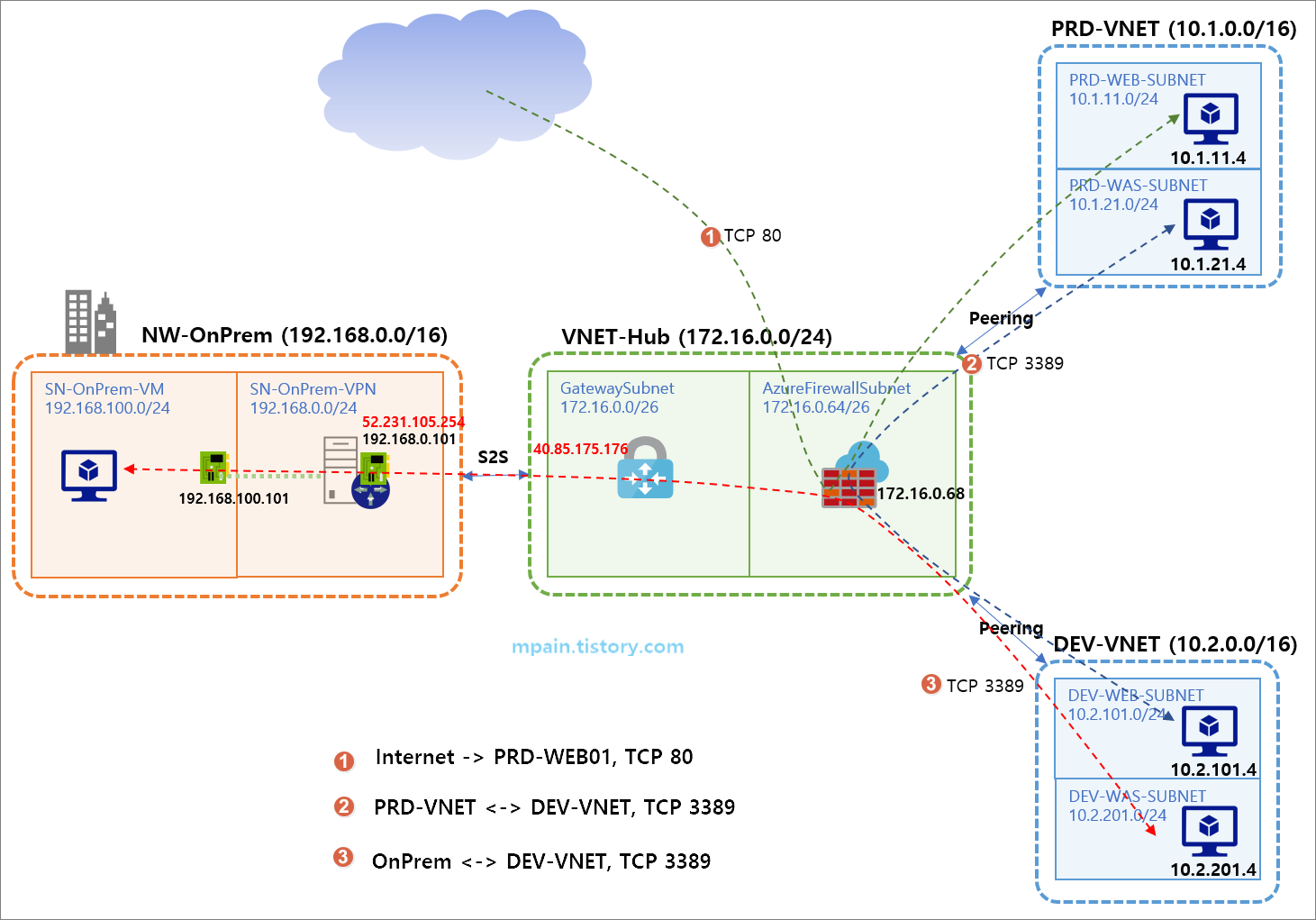
위 테스트 환경 구성은 일반적인 허브-스포크(Hub-Spoke) 구성입니다.
허브 네트워크에 Azure VPN Gateway와 Azure Firewall을 배치하고, 온프레미스와는 S2S VPN으로 연결하고, 다른 Azure 가상 네트워크는 Peering으로 연결합니다.
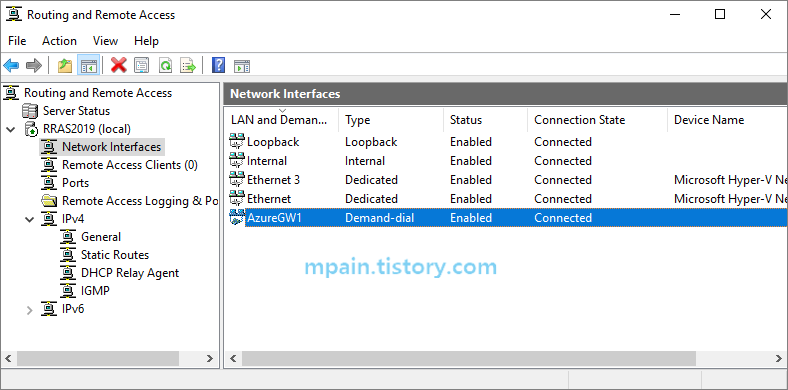
테스트에서는 온프레미스의 Windows Server 2019에 RRAS(Routing and Remote Access Service) 역할을 구성하여 Azure VPN Gateway와 S2S로 연결하였습니다.
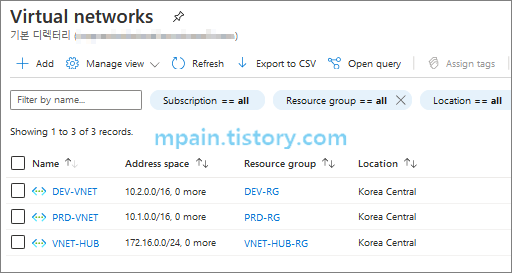
1. 가상 네트워크 생성 및 Peering으로 연결
Azure에 아래와 같이 3개의 가상 네트워크를 만듭니다.
허브 네트워크(VNET-Hub)에 VPN Gateway를 배포하고, 온프레미스와 S2S VPN을 연결합니다. (온프레미스와 S2S VPN 연결에 대한 설명은 생략합니다.)

허브 네트워크(VNET-Hub)와 스포크 네트워크들(PRD-VNET, DEV-VNET)은 Peering으로 연결하였습니다.
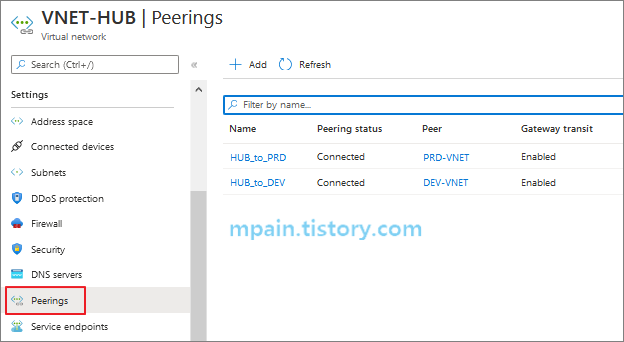
참고로, Peering 옵션에서 Gateway transit을 사용하도록 설정하였습니다.
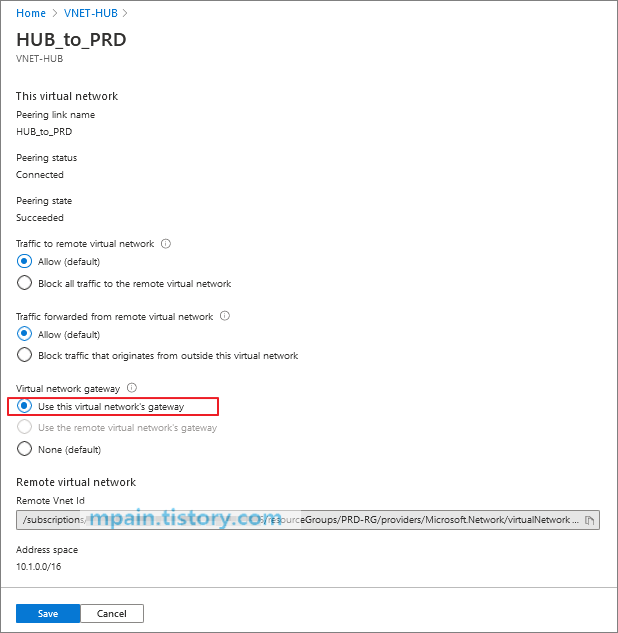
가상 네트워크 구성이 완료된 후 가상 머신을 배포합니다.
2. Azure Firewall 배포
허브 네트워크(VNET-Hub)에 Azure Firewall을 배포합니다. Azure Firewall은 AzureFirewallSubnet이라는 이름의 전용 서브넷에 배포되어야 합니다. 서브넷 사이즈는 /26으로 만듭니다.
Azure Firewall 배포
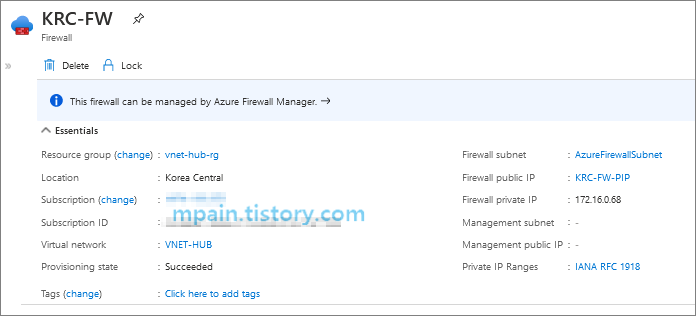
Azure Firewall 배포가 완료되면 Azure Firewall의 Private IP 주소를 확인합니다.
3. 라우팅 테이블 구성 (UDR)
네트워크 간 트래픽이 Azure Firewall을 거치도록 라우팅 테이블을 구성합니다.
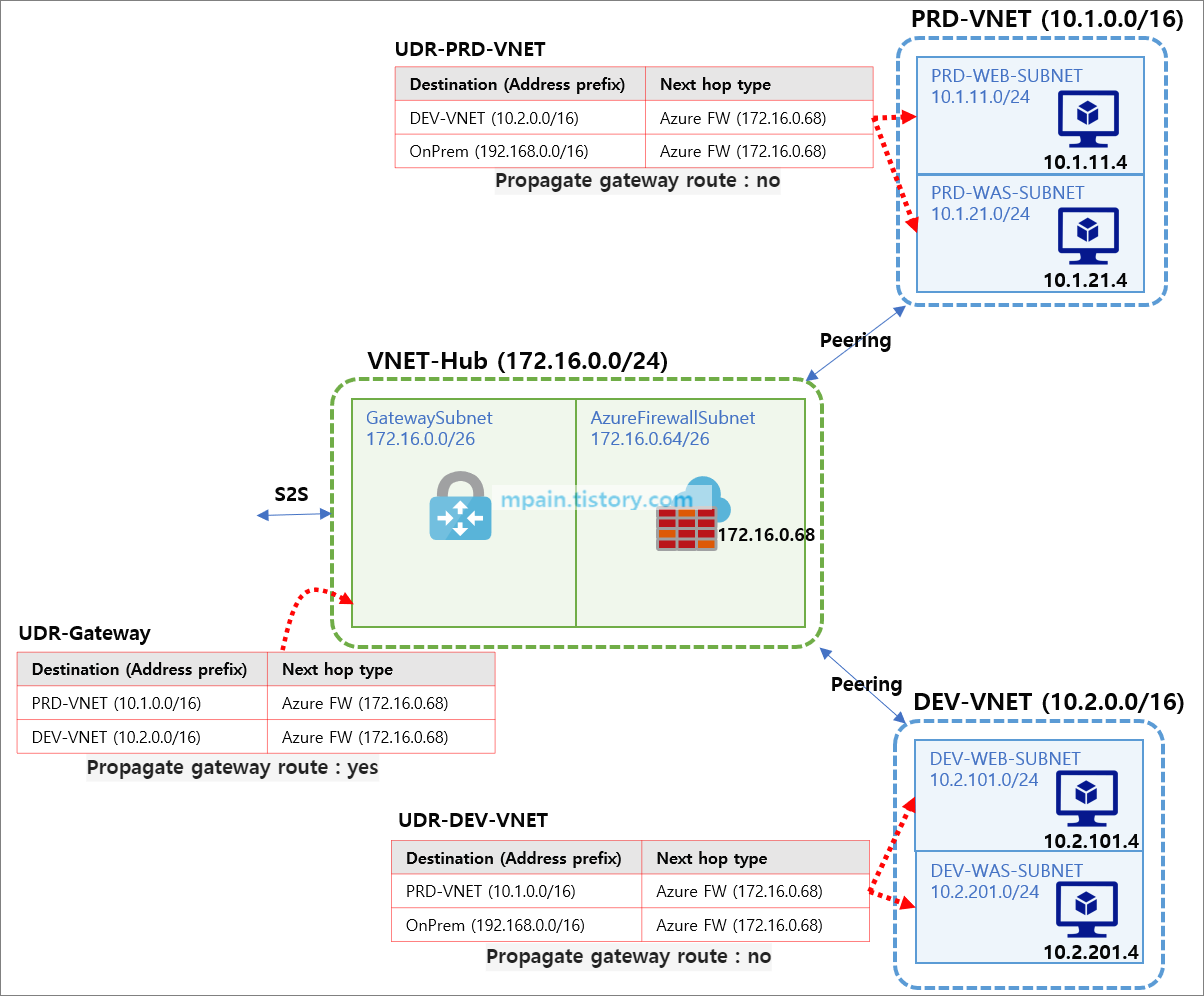
스포크 네트워크들(PRD-VNET, DEV-VNET)은 Next hop을 Azure Firewall로 지정합니다.
GatewaySubnet은 Next hop으로 Azure Firewall을 지정합니다.
4. DNAT 규칙 추가
인터넷에서 PRD-VNET의 WEB VM으로 HTTP (TCP 80) 접속을 허용하는 DNAT 규칙을 Azure Firewall에 추가합니다.
DNAT(Destination NAT) 규칙을 사용하면, 인터넷에서 Azure 가상 네트워크의 VM으로의 직접적인 연결은 차단하고, Azure Firewall의 공인 IP 주소를 통해 Azure VM으로 연결될 수 있도록 구성할 수 있습니다.
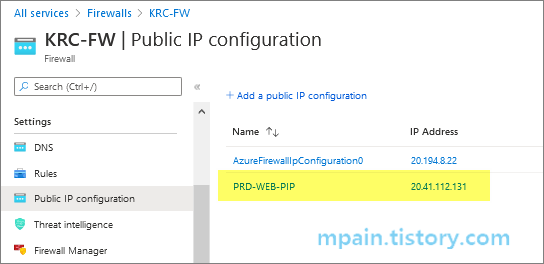
우선 Azure Firewall에 Public IP 주소를 하나 추가합니다.
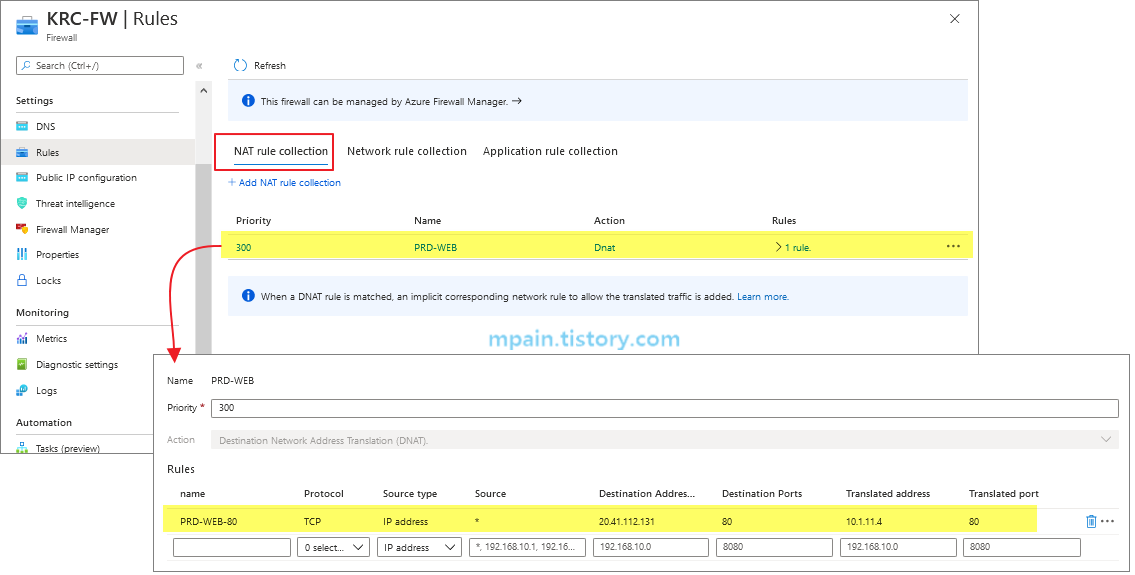
Azure Firewall의 Rule - NAT rule collection에 아래와 같이 DNAT 규칙을 추가합니다.
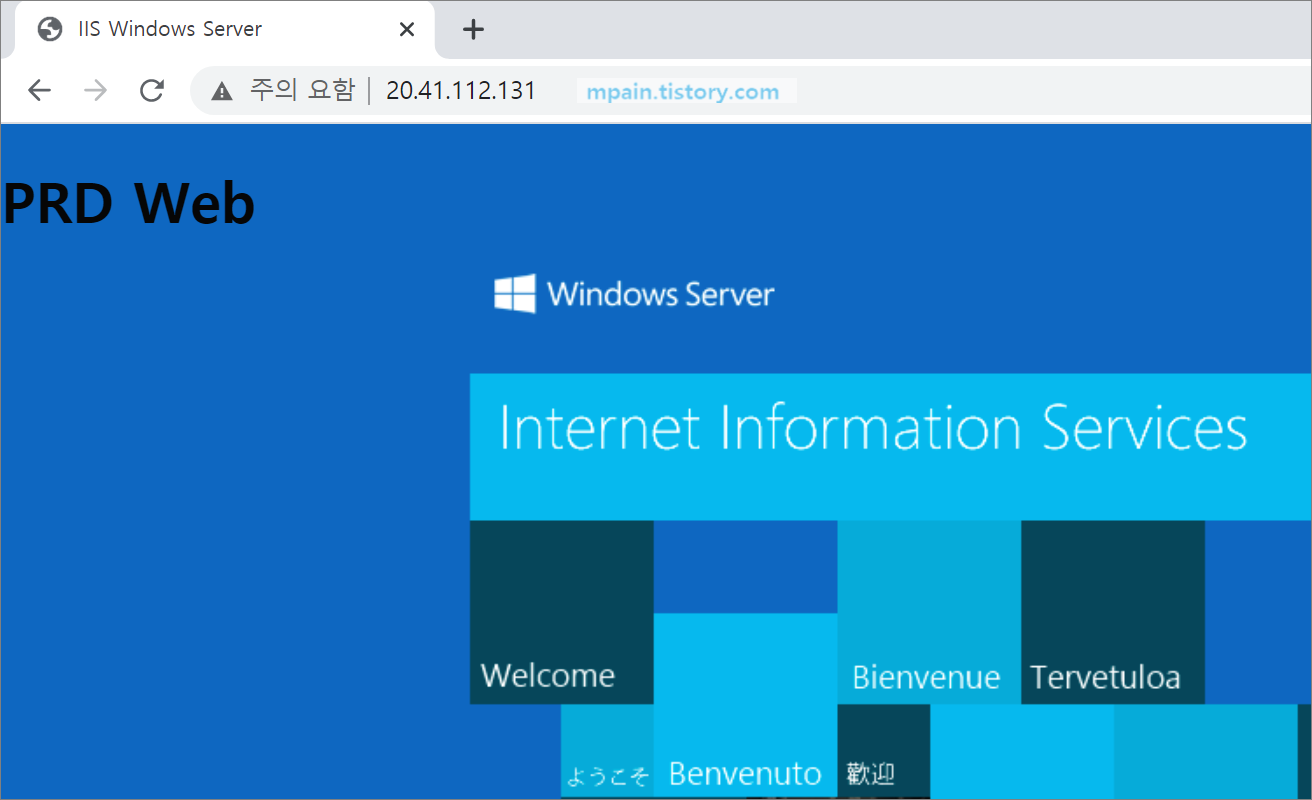
브라우저에서 DNAT 규칙의 공인 IP 주소로 접속해봅니다.
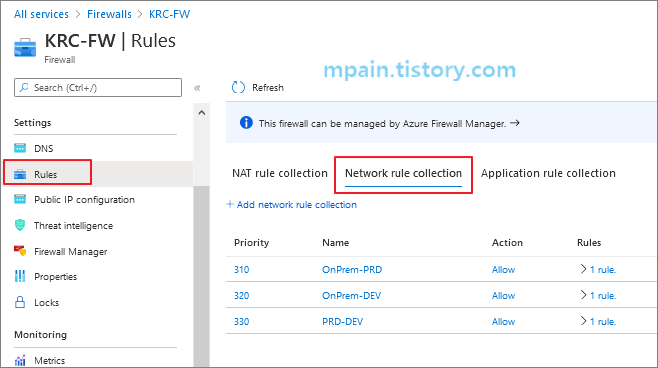
5. 네트워크 규칙 추가
Azure Firewall에 온프레미스와 Azure PRD, DEV 네트워크간 RDP 연결을 허용하는 규칙을 생성합니다.
네트워크 규칙(Network rule)으로 Azure VM으로 들어오고 나가는 네트워크 연결을 허용하거나 차단할 수 있습니다.
Azure Firwall - Rules - Network rule collection에 RDP 허용 규칙을 추가합니다.
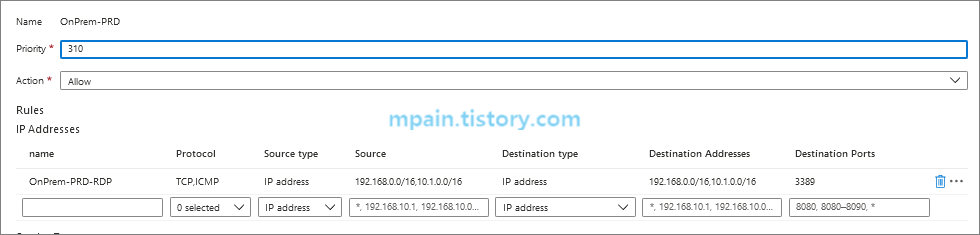
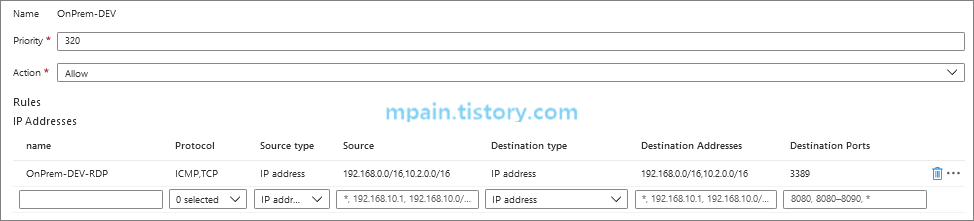
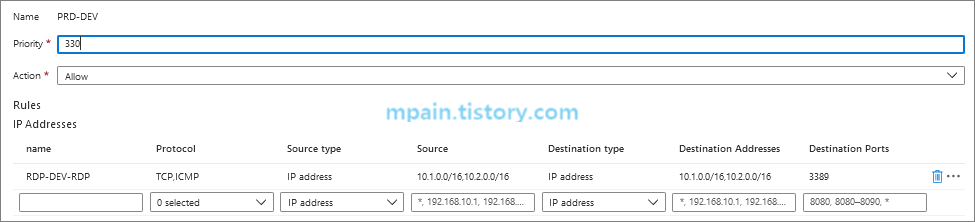
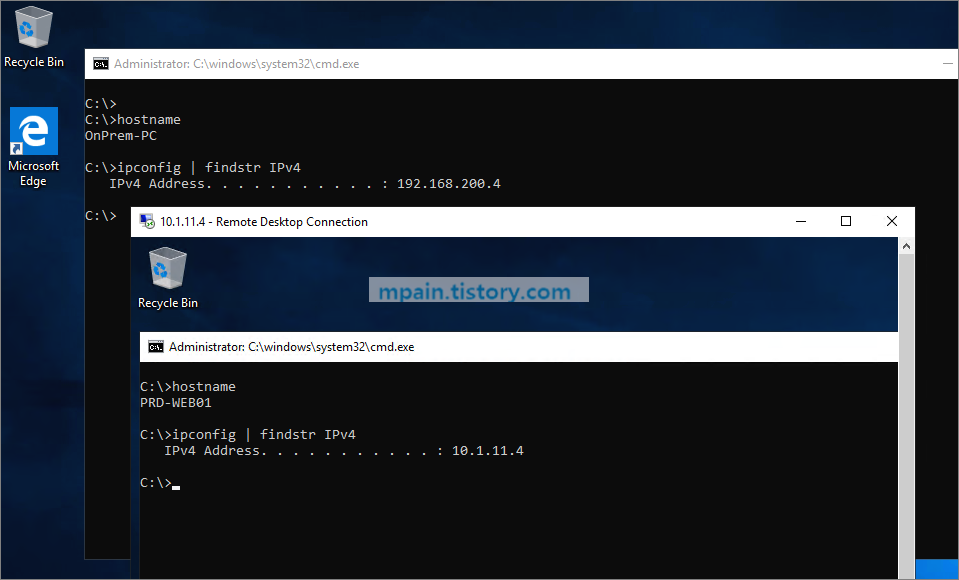
RDP 허용 규칙 추가 후 각 네트워크 간 RDP 연결이 되는지 확인해봅니다.
온프레미스 -> PRD-VNET의 VM으로 RDP 연결
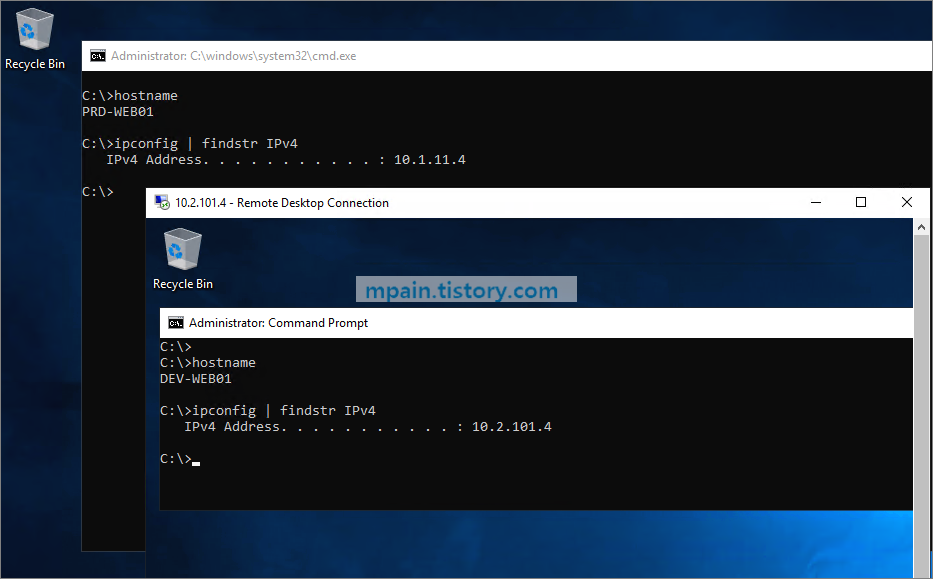
PRD-VNET의 VM에서 DEV-VNET VM으로 RDP 연결
-끝
'IT이야기 > Azure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Windows RRAS를 사용하여 Azure VPN Gateway와 S2S VPN 연결 (0) | 2024.04.24 |
|---|


























